3. CropML Description¶
3.1. Formal definition of a Model Unit in CropML¶
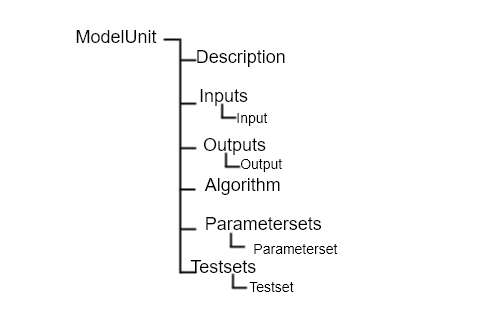
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| ModelUnit |
|
| Description |
|
| Inputs |
|
| Outputs |
|
| Algorithm |
|
| Parametersets |
|
| Testsets |
|
3.1.1. ModelUnit element¶
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE ModelUnit PUBLIC "-//SIMPLACE/DTD SOL 1.0//EN" "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/AgriculturalModelExchangeInitiative/xml_representation/master/ModelUnit.dtd">
<ModelUnit modelid=" " timestep=" " name=" " version="">
....
</ModelUnit>
3.1.2. Description element¶
This element gives the general information on the model and is composed by a set of character elements. It MUST contain Title, Authors, Institution and abstract elements and MAY optionally contain URI and Reference elements.
<ModelUnit modelid=" " timestep=" " name=" " version =" ">
<Description>
<Title>title</Title>
<Authors>authors</Authors>
<Institution>institution</Institution>
<URI>uri</URI>
<Abstract><![CDATA[abstract]]></Abstract>
</Description>
...
</ModelUnit>
3.1.3. Inputs elements¶
The inputs of Model are listed inside an XML element called Inputs within a dictionary structure composed by their attributes which declarations are optional(default, max, min, parametercategory, variablecategory and uri) or required(name, datatype, description, inputtype, unit ) and their corresponding value. Inputs element MUST contain one or more Input elements.
<ModelUnit modelid=" " timestep=" " name=" " version =" ">
...
<Inputs>
<Input name=" " description=" " parametercategory=" " datatype=" " min=" " max=" " default=" " unit=" " uri="" inputtype=" "/>
<Input name=" " description=" " parametercategory=" " datatype=" " min=" " max=" " default=" " unit=" " uri=" " inputtype=" "/>
...
</Inputs>
...
</ModelUnit>
- The required datatype attribute is the type of input value specified in default (the default value in the input), min (the minimum value in the input) and max (the maximum value in the input). It MAY be one type of the set of types used in the existing crop modeling platform.
- The inputtype attribute makes it possible to distinguish the variables and the parameters of the model. So it MUST take one of two possible values: parameter and variable.
- The parametercategory attribute defines the category of parameter which is specified by one of the following values: constant, species, soil and genotypic.
- The variablecategory defines the category of variable depending on whether it is a state, a rate or an “auxiliary” variable. State variable characterize the behavior of the model and rate variable characterizes the changes in state variables.
3.1.4. Outputs element¶
The outputs of Model are listed inside an XML element called Outputs within a dictionary structure composed by their attributes which declarations are:
- optional(variabletype and URI)
- required(name, datatype, description, unit, max and min )
- and their corresponding value
Outputs MUST contain zero or more output elements.
<ModelUnit modelid=" " timestep=" " name=" " version =" ">
...
<Outputs>
<Output name=" " description=" " datatype=" " min=" " max=" " unit=" " uri=" "/>
<Output name=" " description=" " datatype=" " min=" " max=" " unit=" " uri=" "/>
...
</Outputs>
...
</ModelUnit>
3.1.5. Algorithm element¶
<ModelUnit modelid=" " timestep=" " name=" " version =" ">
...
<Algorithm language =""><![CDATA[
...
]]>
</Algorithm>
...
</ModelUnit>
3.1.6. Parametersets element¶
<ModelUnit modelid=" " timestep=" " name=" " version =" ">
...
<Parametersets>
<Parameterset name="" description="" uri = ""/>
<Parameterset name="" description="" >
<Param name="">value</Param>
<Param name="">value</Param>
...
</Parameterset>
...
...
</ModelUnit>
3.1.7. Testsets element¶
<ModelUnit modelid=" " timestep=" " name=" " version =" ">
...
<Testsets>
<Testset name="" parameterset = "" description="" uri = ""/>
<Testset name="" parameterset = "" description="" >
<Test name="">
<InputValue name="">value</InputValue>
...
<OutputValue name="" precision ="">value</OutputValue>
...
</Test>
...
</Testset>
...
</Testsets>
...
</ModelUnit>
3.2. Formal definition of a Composite Model in CropML¶
Vertices are the different models that form the composition.Ports are the inputs and outputs of each model.Edges are directed and connect one output port to an input port of another model.

3.2.1. Inputs element¶
It MUST contain one or more input element which provide a set of independent models entries. If two or more input variables of independent models are the same (same unit, interval, description) a link should be made to one input variable of the composite model.
3.2.2. Outputs element¶
It MUST contain one or more output element which provide a set of independent models outputs or a result of a combination of models .
3.2.3. Composition element¶
It’s a list of models elements which contains a list of links elements. Link provides the mechanism for mapping inputs declared within one modelUnit to output in another modelUnit, allowing information to be exchanged between the various atomic models in the composite model.
3.3. Algorithm element¶
The implementation differs from the platform:
- Discrete Events Models and Formalisms (RECORD)
- Actor model framework (OpenAlea)
- A sequence of algorithmic instructions witch implement the control flow (BIOMA)